How do fintech companies integrate with banks: 7 powerful secrets 2025
Why Fintech-Bank Integration is Revolutionizing Financial Services
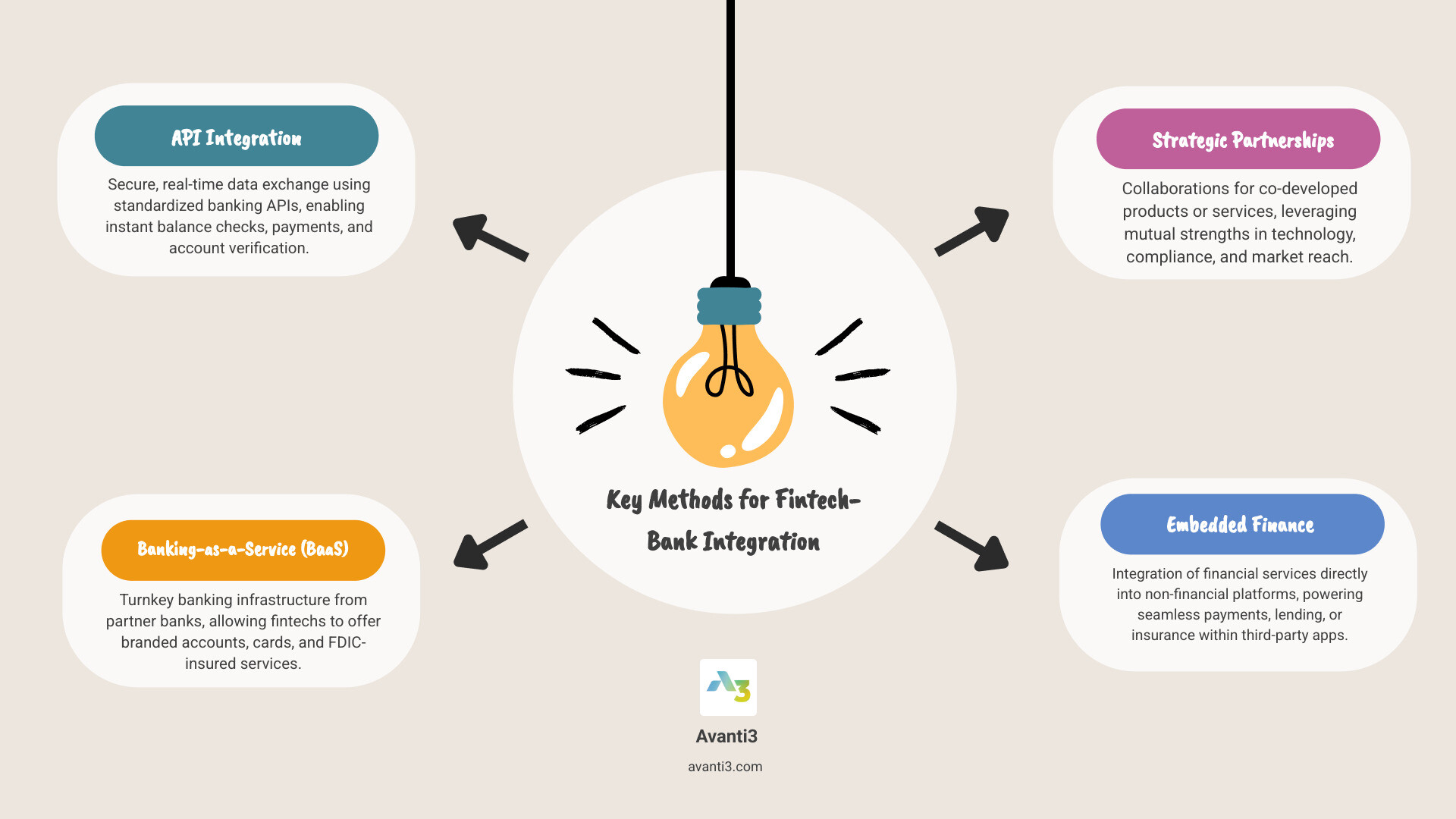
How do fintech companies integrate with banks is becoming one of the most critical questions in modern finance. The integration typically happens through four main approaches:
- API Integration – Direct connections using banking APIs for real-time data access
- Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) – White-label banking infrastructure provided by partner banks
- Strategic Partnerships – Joint ventures for specific products or services
- Embedded Finance – Financial services built directly into non-financial platforms
The numbers tell the story. 65% of banks and credit unions entered fintech partnerships between 2019-2021, while 88% of US consumers now use fintech services. This isn’t just about keeping up with technology – it’s about survival in a market where customers expect instant, seamless financial experiences.
When you split a dinner check with Venmo or get an instant loan approval through an app, you’re experiencing the result of complex integrations between fintech companies and traditional banks. These partnerships combine fintech innovation with banking infrastructure to create services that neither could offer alone.
APIs serve as the “plumbing” that safely connects consumer bank accounts to fintech apps. Through these secure connections, fintech companies can verify account balances, process transactions, and provide personalized financial insights – all while banks maintain regulatory compliance and customer trust.
How do fintech companies integrate with banks glossary:
Understanding How Do Fintech Companies Integrate with Banks
Finance has changed completely in just ten years. Remember when getting a loan meant sitting in a stuffy bank office for hours? Now you can get approved while waiting for your coffee to brew.
How do fintech companies integrate with banks has become the secret sauce behind this change. It’s about building bridges between traditional banks with their rock-solid infrastructure and nimble fintech companies with fresh ideas and sleek user interfaces.
The Federal Reserve study on bank-fintech partnerships shows how essential these partnerships have become for banks to remain relevant in a world where customers expect everything to be instant and intuitive.
Core Integration Models
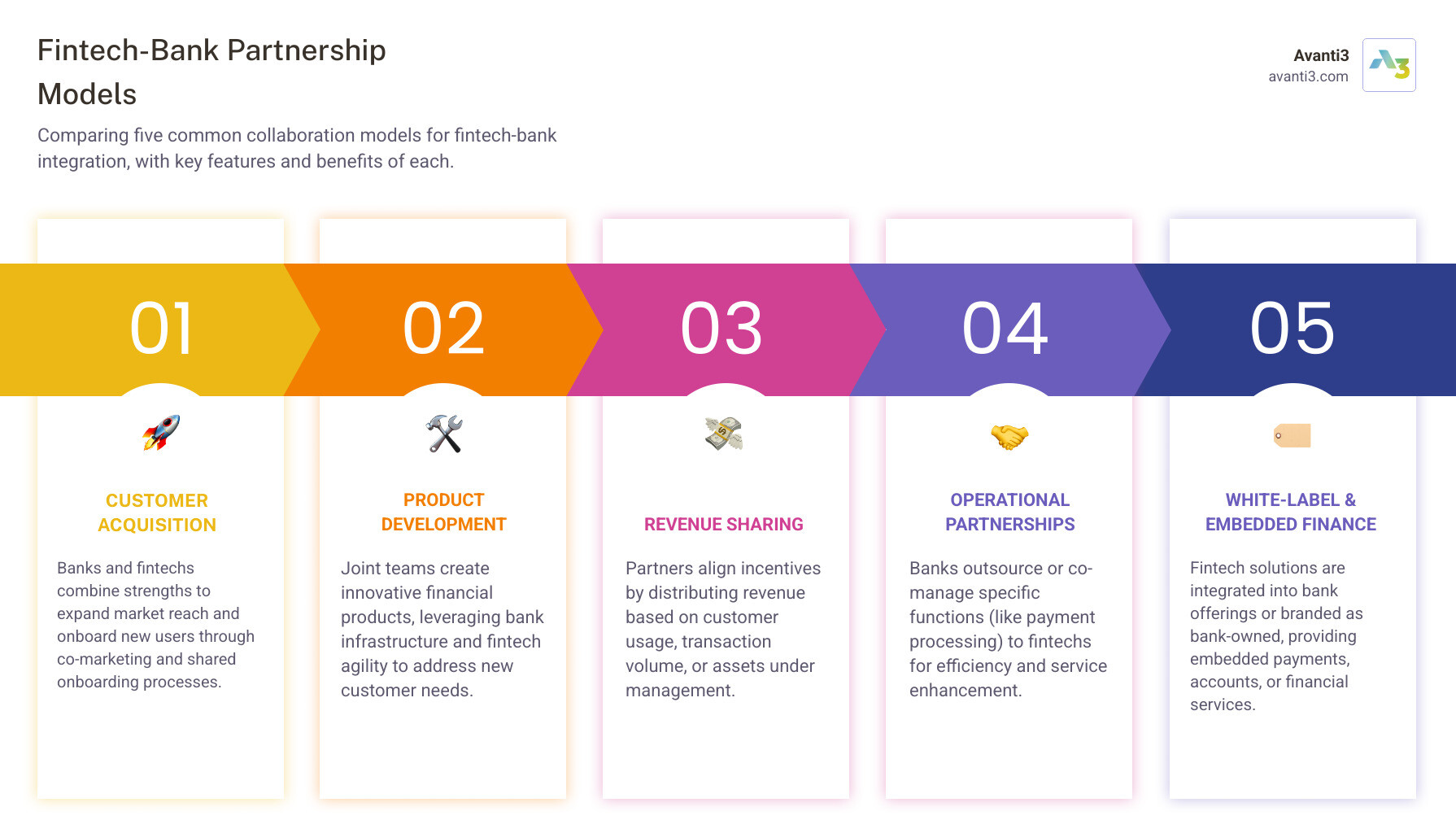
Operational partnerships are like having a specialist handle one specific job really well. A bank might partner with a fintech to streamline loan approvals while keeping everything else in-house.
Technology partnerships go deeper into infrastructure. Banks provide core systems and regulatory framework, while fintechs create the apps and user experiences customers interact with. This approach has reduced monthly reconciliation time from 10 days to just 2.5 days in many cases.
Strategic alliances represent the most collaborative approach, where both parties work together to create something entirely new. These partnerships often result in innovative products that neither company could have developed alone.
White-label solutions offer the most straightforward path to market. Banks can offer fintech-developed products under their own brand, launching new services in months rather than years.
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) Framework
Banking-as-a-Service has revolutionized how do fintech companies integrate with banks by making banking infrastructure available like a utility. Through BaaS platforms, startups can access FDIC insurance, regulatory compliance frameworks, and payment processing capabilities without spending years navigating complex banking regulations.
This model has enabled incredible innovation in embedded finance. E-commerce sites now offer instant financing at checkout, ride-sharing apps provide immediate payouts to drivers, and subscription services handle recurring payments seamlessly.
The real magic of BaaS is speed. What used to take 18-24 months to bring to market can now be accomplished in 3-6 months, dramatically reducing both risk and time-to-revenue.
The Technical Foundation: APIs and Infrastructure
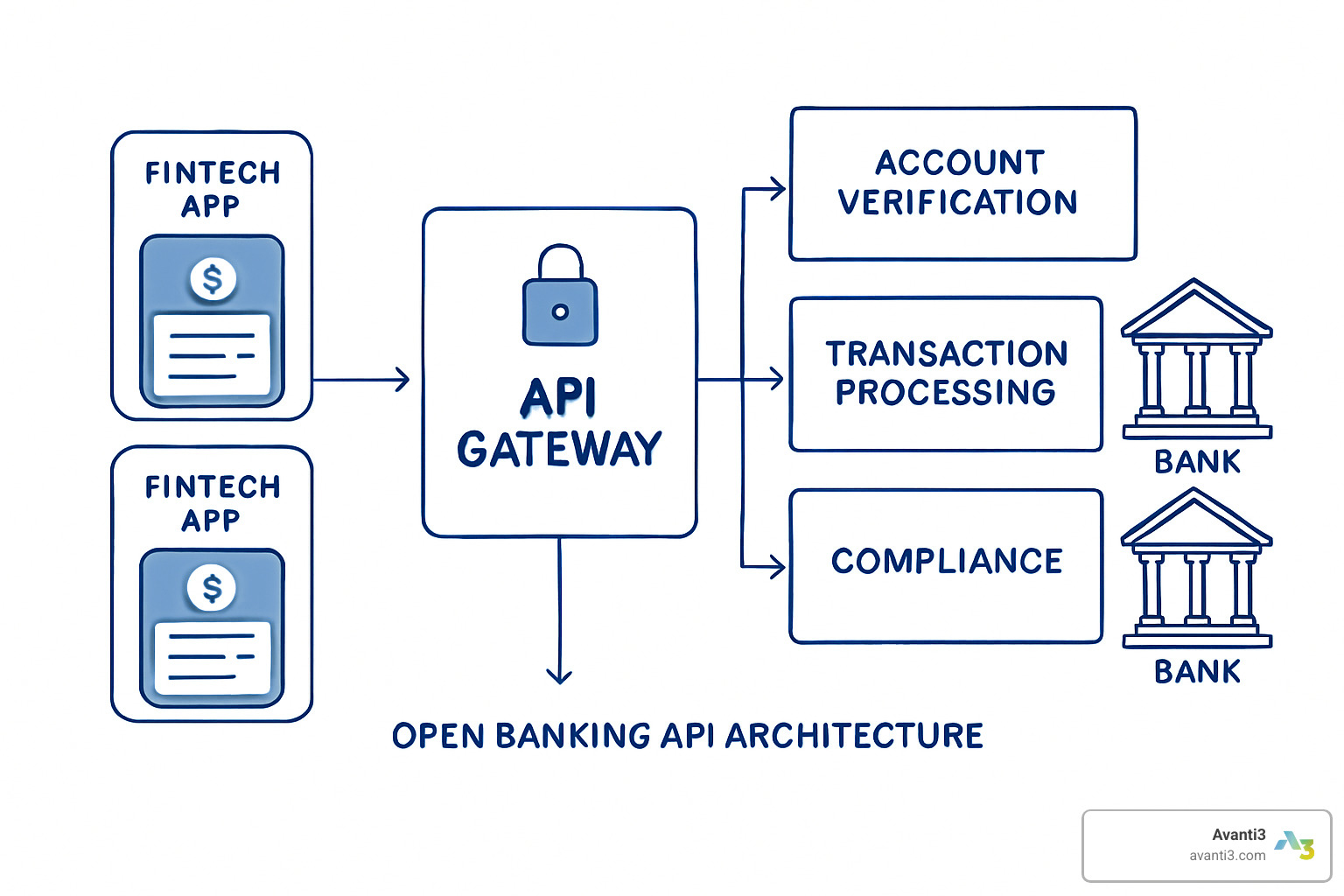
APIs are the digital bridges that make how do fintech companies integrate with banks possible. These Application Programming Interfaces are like translators that help different computer systems talk to each other securely and instantly.
When you check your account balance on a budgeting app or send money through a payment service, you’re experiencing API integration. Behind the scenes, your fintech app is having a quick conversation with your bank’s computer system.
Modern banking APIs work like a well-organized library. Each banking function lives in its own section – account verification, payment processing, transaction history. This modular approach means fintech companies can access exactly what they need without getting into areas they shouldn’t see.
Over 50% of bank connections now happen through APIs, with transactions processing in milliseconds. That’s why you can instantly see if a payment went through or get real-time fraud alerts.
How Do Fintech Companies Integrate with Banks Through APIs
API endpoints serve as specific digital addresses where fintech apps send their requests. Think of them like different windows at a bank – one for account verification, another for balance checks, and another for processing payments.
When you use a personal finance app that shows all your accounts in one place, that’s data aggregation at work. The app sends requests to multiple banks through their APIs and presents everything in a single dashboard.
Transaction processing APIs handle the heavy lifting when you move money. Account verification APIs provide instant confirmation that you own an account and have enough money for a transaction.
The average person now uses 3-4 different fintech apps to manage their money, and every single one relies on these API integrations to work properly.
Security and Authentication Layers
Security is built into every layer of how do fintech companies integrate with banks. Encryption standards like TLS scramble your data as it travels between apps and banks. Identity verification processes use multi-factor authentication and biometric verification to prevent fraud.
AML screening and KYC compliance happen automatically through API integrations. OAuth 2.0 has become the gold standard for authentication, allowing you to grant specific permissions to apps without sharing your actual banking passwords.
All these security layers work together seamlessly, creating a system that’s both incredibly secure and surprisingly user-friendly.
Partnership Models and Implementation Strategies
How do fintech companies integrate with banks involves diverse partnership models, each bringing unique strengths to create something neither could achieve alone.
Customer acquisition partnerships help banks access tech-savvy fintech users while fintechs gain credibility from established banking relationships. Product development collaborations combine banks’ infrastructure and regulatory expertise with fintechs’ innovation and development speed.
Embedded finance is projected to generate $230 billion in revenue by 2025, representing a tenfold increase from 2020 levels. Revenue sharing models keep everyone motivated through arrangements that distribute income based on actual usage and performance.
How Do Fintech Companies Integrate with Banks: Step-by-Step Process
The due diligence phase involves mutual evaluation of financial health, regulatory track record, and technical capabilities, typically taking 2-4 weeks.
Technical integration begins in sandbox environments where teams can safely test API functionality and optimize performance. Compliance validation ensures every regulatory requirement is met before launch.
Deployment phases follow a gradual approach starting with limited user groups before full rollout. What used to require 4-6 weeks can now be accomplished in just one week for standard implementations.
Embedded Finance and White-Label Solutions
Embedded finance brings banking services directly into platforms people already use. Embedded payments eliminate frustrating redirects to external payment pages, dramatically improving conversion rates.
Branded accounts allow retail companies to offer store credit cards, ride-sharing apps to provide driver payment accounts, and freelance platforms to offer instant payout services. Checkout integration has revolutionized online shopping by embedding payment capabilities directly into the purchase flow.
Our research reveals that 76% of consumers are more likely to use an app when they can sign up and access it instantly without lengthy registration processes.
At Avanti3, we see fascinating parallels between traditional embedded finance and the emerging Web3 ecosystem. Our Web3 Platform Solutions apply similar integration principles to seamlessly blend conventional financial services with innovative blockchain-based rewards and community engagement tools.
Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
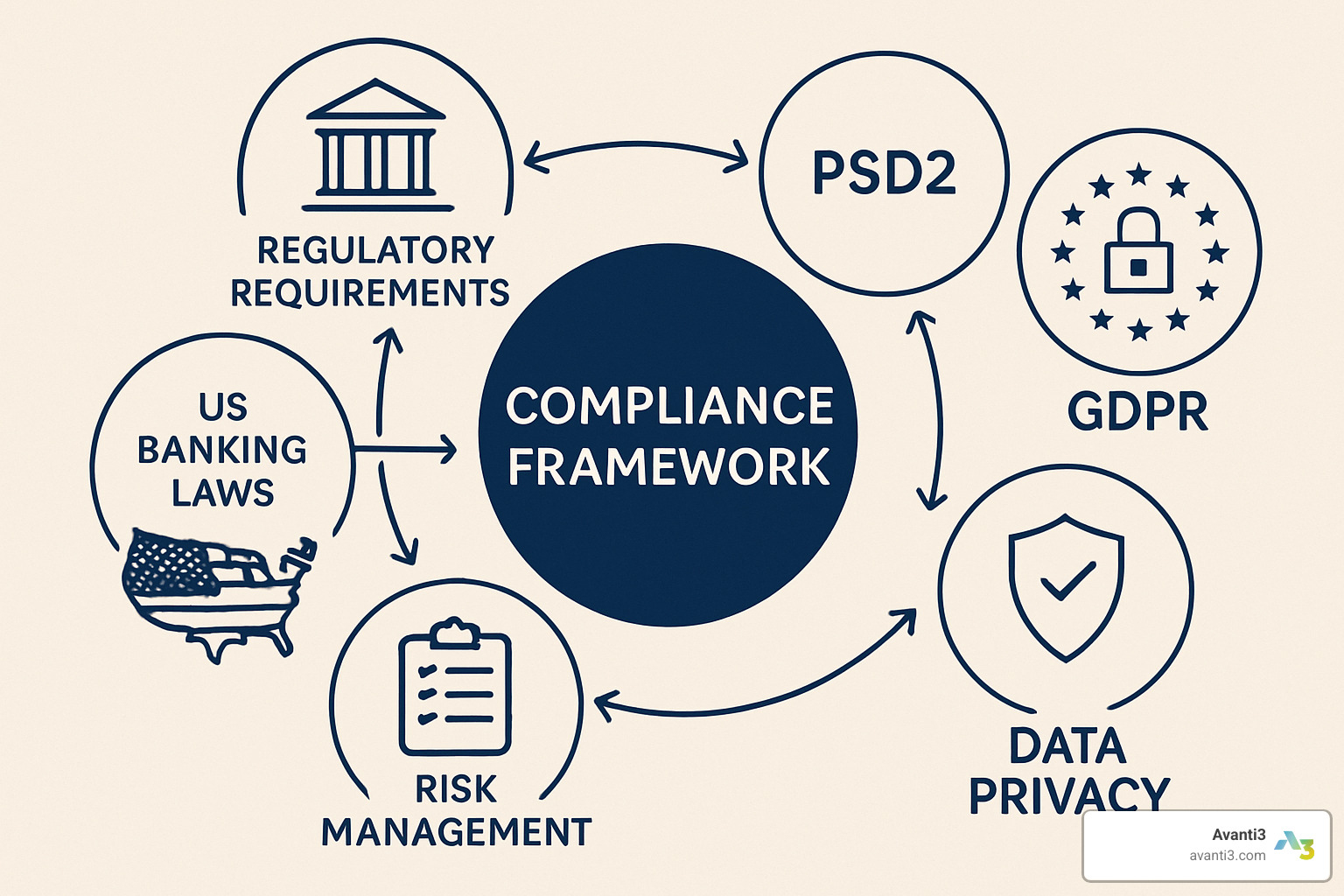
Regulatory compliance isn’t just a checkbox exercise in how do fintech companies integrate with banks – it’s the foundation that makes these partnerships possible.
PSD2 regulations in Europe have created clear rules for open banking, requiring banks to provide secure API access to authorized third parties. GDPR requirements add complexity when customer data crosses between fintech apps and banks, requiring proper consent and secure handling.
Risk assessment processes help both sides understand responsibilities, while ongoing monitoring systems work behind the scenes to catch issues before they become problems. According to KPMG fintech funding data, this due diligence process has become more streamlined as industry standards mature.
Compliance Challenges and Solutions
Legacy systems represent the biggest challenge – imagine connecting a smartphone to a 1990s computer. The solution involves building translation layers that can speak both old and new languages fluently.
Data privacy requirements now include sophisticated consent management tools that let customers control exactly what information gets shared. Regulatory reporting capabilities must be built into every integration from day one, with smart platforms automatically generating required reports.
Audit trails capture every interaction between fintech applications and banking systems, becoming crucial evidence during regulatory examinations.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
Fraud detection systems use artificial intelligence to spot suspicious patterns in real-time, learning from millions of transactions to identify unusual activity. Transaction monitoring capabilities watch for money laundering while keeping normal transactions flowing smoothly.
Customer screening processes verify identities and check government watchlists during account setup, happening in seconds rather than days. Operational risk management prepares for system failures through redundant systems and disaster recovery procedures.
The complexity of compliance enables the trust that makes fintech innovation possible. When customers know their data and money are protected, they’re more willing to try new financial services.
Implementation Timelines and Success Factors
Realistic timelines make the difference between smooth partnerships and frustrating delays when planning how do fintech companies integrate with banks.
The planning phase typically takes 2-4 weeks for aligning technical requirements and business objectives. Technical development and integration usually spans 4-8 weeks, though simple balance checks might complete in days while comprehensive solutions require several months.
Testing and validation consumes 2-4 weeks in sandbox environments. The final deployment and monitoring phase takes 1-2 weeks with gradual rollout to larger user groups.
Our research shows that consumers linked via open APIs spend up to 28% more per month and transact up to 7% more frequently. These business improvements justify the investment in proper integration.
Common Integration Challenges
Legacy infrastructure remains the biggest headache – many banks operate on mainframe systems requiring complex middleware for modern API architectures. Data standardization creates complexity as different systems use incompatible formats.
Latency issues can kill user experience when API calls require multiple system interactions. Multi-bank complexity increases exponentially when fintech companies integrate with multiple banking partners, each bringing different specifications and requirements.
Best Practices for Successful Integration
Documentation standards reduce development time and help troubleshoot issues during testing. Version control systems manage API changes without breaking existing integrations.
Monitoring systems provide early warning systems that prevent small issues from becoming major problems. Error handling procedures must gracefully manage inevitable system failures with retry mechanisms and clear user communication.
The most successful integrations treat these practices as fundamental requirements that determine whether partnerships will thrive over time.
Frequently Asked Questions about Fintech-Bank Integration
What are the main types of fintech-bank partnerships?
When we look at how do fintech companies integrate with banks, there are four main partnership styles:
API Integration Partnerships provide direct connections to bank infrastructure using secure APIs for real-time data and instant transaction processing.
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) Partnerships let fintechs use a bank’s white-label infrastructure to offer checking accounts or payment tools while staying compliant.
Strategic Alliances involve banks and fintechs working together to develop new products, expand into new markets, or launch co-branded services.
Embedded Finance Partnerships weave financial services directly into non-financial platforms – like paying for a ride or subscription without leaving your favorite app.
How long does it typically take to integrate a fintech with a bank?
Timelines for how do fintech companies integrate with banks vary significantly based on complexity.
Simple API integrations like checking balances or verifying accounts can be completed in 1-2 weeks. Standard integrations for payment processing or data aggregation usually take 4-8 weeks.
Full BaaS setups or multi-bank connections stretch to 3-6 months. Large-scale strategic partnerships with new product development can require 6-12 months.
Thanks to modern API architectures, integration times keep shrinking – what used to take a month can sometimes be done in just a week.
What regulatory requirements must be met for fintech-bank integration?
Regulations are crucial for how do fintech companies integrate with banks to keep customers safe.
Data protection requires GDPR compliance for European customers, including clear consent and careful personal data handling. Financial regulations like PSD2 set open banking standards, while AML and KYC screening prevent illegal activity.
Security standards mandate encryption, strong authentication, and detailed audit trails. Reporting obligations require banks and fintechs to maintain detailed records and monitor transactions.
Consumer protection ensures customers know what data is shared, how it’s used, and how to resolve disputes.
For more insights on compliance, see our page on banking compliance for fintech integrations.
Conclusion
The journey of how do fintech companies integrate with banks has been remarkable. We’ve gone from clunky, disconnected systems to a world where you can split a dinner bill, get a loan approval, and invest your spare change while waiting for your coffee.
With 88% of US consumers using fintech services and 65% of banks in fintech partnerships, this is the new reality of financial services. Embedded finance expected to hit $230 billion by 2025 shows we’re just getting started.
What makes these integrations successful isn’t just fancy technology – it’s creating effortless experiences while maintaining security and trust. The best partnerships combine fintech creativity with banking infrastructure and regulatory expertise.
Regulatory compliance and risk management make these partnerships possible. Without proper frameworks for data protection and fraud prevention, even the most innovative ideas would never reach consumers.
At Avanti3, we see these integration principles playing out in Web3. Our approach to Digital Experience Design applies lessons from successful fintech-bank partnerships to blockchain, NFTs, and community engagement platforms. The core challenge remains: how do you integrate new technologies with existing systems while creating experiences people want to use?
Looking ahead, AI-powered personalization, blockchain settlement systems, and IoT payment experiences are on the horizon. Organizations that understand integration fundamentals today will capitalize on tomorrow’s opportunities.
Whether you’re building a fintech startup or exploring embedded finance, successful integration is about more than connecting systems. It’s about connecting with people, solving real problems, and building trust through every interaction.
The future of financial services isn’t just digital – it’s integrated, seamless, and surprisingly human.







