Why Fintech Integration with Banks is Reshaping Finance
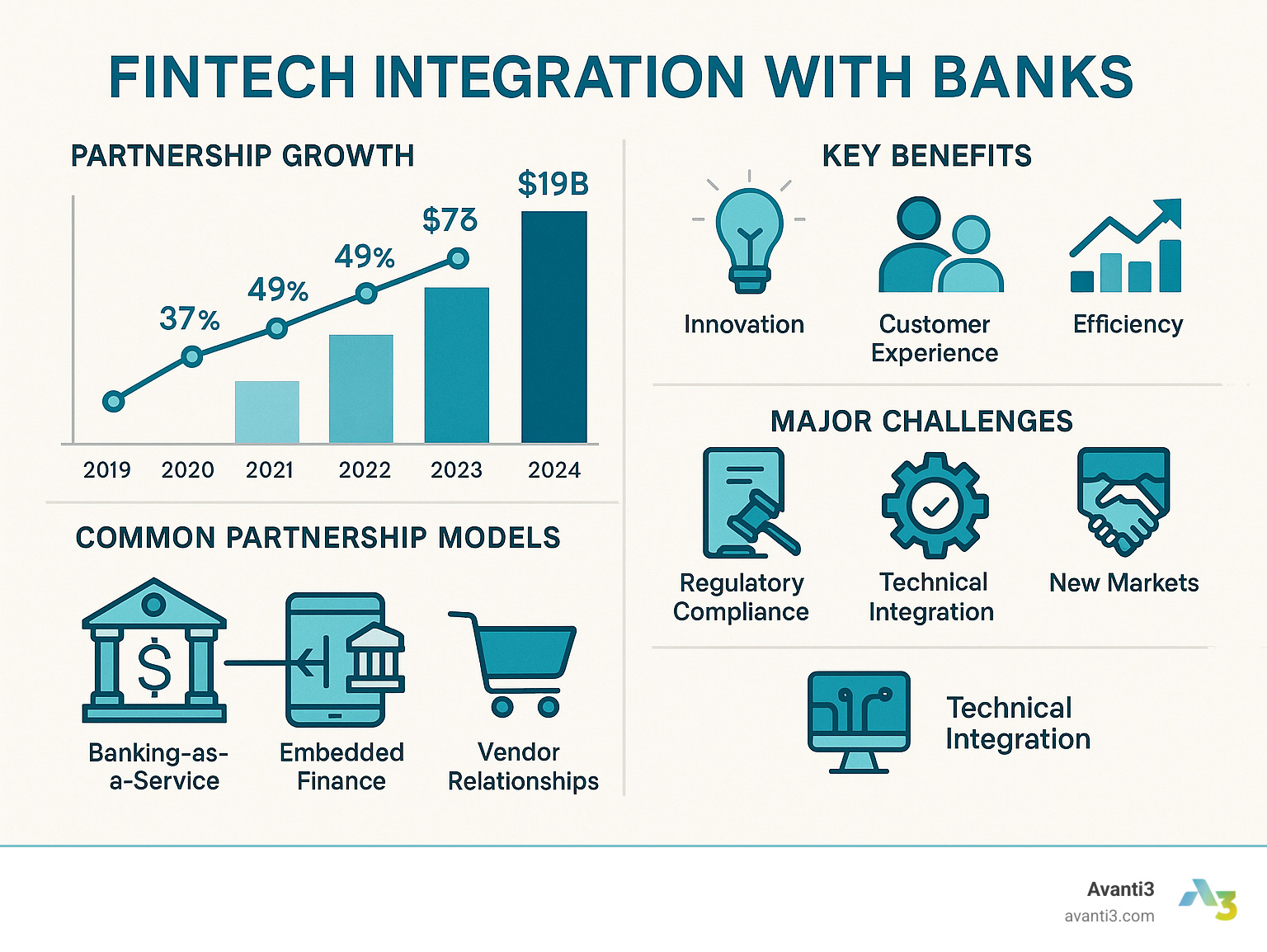
Fintech integration with banks has evolved from a competitive battleground into a collaborative partnership, creating strategic benefits for everyone involved. This integration involves various partnership models like Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) and embedded finance, offering key benefits such as faster innovation and improved customer experience. However, it also presents challenges like regulatory compliance and technical problems, which require clear governance and due diligence to overcome.
The numbers tell a compelling story. Nearly two-thirds of all banks and credit unions have entered into at least one fintech partnership in the last three years, with average investments growing significantly. The global fintech market’s valuation underscores this trend, with projections expecting it to reach $917 billion by 2032.
This isn’t just about money; it’s about survival and innovation. Traditional banks bring regulatory expertise and customer trust, while fintechs contribute agility and cutting-edge technology. Together, they create solutions neither could achieve alone, meeting new customer expectations. With 48% of Americans now relying on mobile banking, adapting is no longer optional.
I’m Samir ElKamouny AV, and I’ve spent years helping businesses steer complex technological changes through strategic partnerships. I understand that fintech integration with banks requires balancing innovation with security and speed with compliance. Let me guide you through this fascinating evolution.
The Courtship: Why Banks and Fintechs Are Drawn to Each Other
The partnership between traditional banks and fintech startups is a classic case of opposites attracting. Banks offer stability, trust, and regulatory know-how, while fintechs bring speed, innovation, and a fresh approach to customer needs. This collaboration is reshaping the financial landscape.
The growth is explosive: fintech startups in the Americas surged from 5,868 in 2018 to nearly 14,000 in 2024. This revolution is forcing traditional banks to adapt or risk becoming obsolete.
What’s driving this partnership? Customer-centric solutions are at the heart of it. Today’s customers, especially younger generations, expect financial services to be as intuitive and instant as their favorite apps. When 90% of consumers report that fintech has helped them, it’s clear that real value is being created.
Other key drivers include:
- Operational Efficiency: Fintechs introduce automation and AI-driven security, streamlining clunky back-office processes for banks.
- Speed to Market: Partnering with agile fintechs allows banks to launch cutting-edge services much faster than they could on their own.
- Financial Inclusion: With 4.2% of American households still unbanked, fintech’s mobile-first approach can extend financial services to underserved communities.
The global fintech market’s journey to a projected $917.17 billion by 2032 highlights the massive scale of this opportunity.

Enhancing the Customer Experience
Fintechs have revolutionized customer expectations. The days of visiting a branch for simple transactions are over. With mobile banking adoption at 48% among Americans, customers now demand omnichannel solutions with user-friendly interfaces that work seamlessly across all devices.
Beyond slick apps, customers want personalized financial advice, faster services, and reduced friction in every interaction. Integrating AI and machine learning, often through fintech partnerships, allows banks to analyze spending patterns, predict needs, and offer custom solutions. The focus on digital experience design is crucial for turning customers into loyal advocates.
Achieving Operational Excellence
Behind the scenes, fintech integration with banks is changing operations. The most immediate benefit is cost reduction through the automation of manual tasks. For example, we’ve seen companies cut monthly reconciliation time from 10 days to just 2.5 days.
Instead of a complete overhaul, banks use fintechs for legacy system modernization, gradually adding new capabilities. Key improvements include automation in loan processing, improved data analytics for smarter decisions, and AI-driven security to combat fraud. This has led to 37% of banks reporting significant improvements in loan productivity.
By streamlining back-office processes with solutions like AI customer engagement, banks become leaner and more competitive, empowering their employees to focus on higher-value work.
Defining the Relationship: Popular Partnership Models
Bankfintech partnerships have evolved into sophisticated collaboration models, each with different levels of commitment. Banks can choose a structure that aligns with their strategic goals, from simple vendor relationships to deep integrations.
Common models include:
- Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS): Lets fintechs offer financial products by plugging into a bank’s regulated infrastructure via APIs. (See Wikipedias overview of BaaS for more background.)
- Embedded Finance: Weaves financial services seamlessly into non-financial apps, like “buy now, pay later” options at checkout.
- White-Label Solutions: Allows banks to license and brand fintech-built platforms as their own for quick digital upgrades.
- Referral Partnerships: Banks and fintechs recommend each other’s services to their respective customers.
- Fintech as a Vendor: Banks purchase specific technology, like fraud detection software, from fintechs.
- Direct Investment and Acquisition: Banks take ownership stakes in or acquire fintechs to gain control over their technology and talent.
Understanding the nuances between these models is key. Here’s a comparison of the most popular approaches:
| Feature | Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) | Embedded Finance | Fintech as a Vendor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Who owns the customer? | Fintech/Brand (bank is the backbone) | Non-financial app/platform (bank is behind the scenes) | Bank (fintech provides a tool) |
| Regulatory burden | Primarily with the bank (fintech must comply with bank) | Primarily with the bank/provider | Primarily with the bank |
| Speed of implementation | Moderate to Fast | Moderate to Fast | Fast (for specific tools) |
| Core value prop | Enables non-banks to offer financial products | Integrates finance into everyday non-finance contexts | Improves bank’s internal processes or specific services |
| Example | Fintech offers checking accounts via partner bank’s APIs | Ride-sharing app offers instant driver payouts | Bank buys fraud detection software from a fintech |
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) and APIs
BaaS has become a cornerstone of fintech integration with banks. It allows banks to monetize their infrastructure and regulatory expertise by ‘renting’ them out. The magic happens through APIs the digital plumbing that allows different software systems to communicate securely.
However, 81% of surveyed banks struggle with API experience and maturity, making API development a key competitive differentiator. As we’ve explored in How APIs are changing digital banking, they are the backbone of modern finance. Driven by Open Banking regulations, BaaS creates a winwin: banks generate new revenue while fintechs innovate on top of a solid regulatory foundation.
Embedded Finance: The Seamless Integration
Embedded finance makes financial services so seamless they almost disappear into our daily activities. Instead of visiting a separate banking app, financial services appear exactly when and where they’re needed, like instant financing on a checkout page.
This approach expands a bank’s reach indirectly, generating transactions and revenue from customers on e-commerce or business software platforms. With embedded finance services projected to generate $230 billion in revenue by 2025, the opportunity is immense. The goal is to make financial transactions feel effortless, giving banks access to new customer segments. You can learn more from our insights on More on Embedded Finance.
Navigating the Complexities of Fintech Integration with Banks
While bank-fintech integration offers immense potential, it’s a complex process with significant challenges. Successful partnerships require diligent work to steer regulatory, technical, and cultural problems.
The foundation of any partnership is thorough due diligence. Banks must deeply investigate a fintech’s business model, financial health, and security protocols. This isn’t a one-time check; third-party risk management requires ongoing monitoring, clear governance frameworks, and solid contractual agreements that define responsibilities.

Regulatory Scrutiny and Compliance Challenges
The regulatory landscape is a minefield. Regulatory bodies like the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), FDIC, and Federal Reserve are scrutinizing these partnerships intensely. The numbers are sobering: 90% of sponsor banks struggle with compliance in their fintech partnerships, with some even ending partnerships in 2024 due to the regulatory pressure.
Regulators are especially concerned about BSA/AML compliance (Bank Secrecy Act/Anti-Money Laundering) and consumer protection. When a fintech partner fails to meet these standards, the bank is held accountable. Data privacy regulations add another layer of complexity, as all customer information must be rigorously protected. With scrutiny expected to increase, banks must prioritize compliance now.
Technical and Cultural Problems in Fintech Integration with Banks
Beyond regulations, making systems and cultures work together is a major challenge. Legacy system clashes are a primary technical headache, as older banking cores weren’t designed for the modern, API-driven world. This leads to costly and prolonged integration projects.
As noted, 81% of surveyed banks cited a lack of API experience as a hurdle. Without API maturity, communication between systems breaks down. Other technical issues include ensuring data security across shared systems and planning for scalability as the partnership grows.
Then there are the cultural differences. Fintechs are typically agile and risk-tolerant, while banks are more cautious and methodical. This “Monkey vs. Gorilla” dynamic can create friction that undermines a partnership’s success. It’s telling that only 6% of senior bank executives felt their collaborations achieved the targeted ROI, often due to a poor cultural fit or a failure to properly measure success beyond direct revenue.
Making It Last: Best Practices for a Successful Partnership
A successful bank-fintech partnership requires more than initial enthusiasm; it needs ongoing commitment, clear communication, and a shared strategic vision to thrive long-term. This vision must have strong leadership buy-in from both sides, with consistent resources and support.
Ongoing monitoring is essential to track performance, identify issues early, and adapt to market changes. A joint roadmap ensures both parties remain aligned on future development, preventing strategic drift. Perhaps most importantly, banks must foster an innovation culture that accepts the fintech’s entrepreneurial spirit, encouraging agility and experimentation. For more on this, explore More on our Technology approach.
The Playbook for a Strong Fintech Integration with Banks
Success in fintech integration with banks requires a structured approach that addresses both technical and human elements.
- Start with a pilot program: Test the technology, processes, and cultural fit on a small, manageable project before a full-scale rollout.
- Establish a joint governance committee: Create a formal body with key stakeholders from both sides to oversee the partnership, resolve conflicts, and maintain strategic alignment.
- Define success metrics upfront: Agree on measurable KPIs—like customer satisfaction, cost reductions, or revenue growth—to track progress objectively.
- Ensure cultural alignment through joint workshops: Proactively bridge cultural gaps with joint training and workshops to build trust and align working styles.
- Plan for scalability from day one: Ensure the fintech’s solution can handle the bank’s transaction volumes and growth, which requires robust architecture planning.
The Future is Collaborative: How AI and Web3 are Shaping the Next Chapter
The next chapter of fintech integration with banks is being written by emerging technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI) and blockchain. AI is revolutionizing finance by enabling sophisticated fraud detection, personalizing advice, and automating complex processes.
Blockchain offers improved security and transparency for financial transactions and is enabling innovations like the tokenization of assets (Real World Assets or RWA). These technologies are driving trends toward real-time and invisible payments, creating effortless experiences that boost customer loyalty.
At Avanti3, we are pioneering new engagement models with these advanced technologies. Our Web3 Platform Solutions leverage NFTs, AR/VR, and AI to create unique digital experiences and fintech solutions.
The future for banks and fintechs is collaborative. The lines between them will continue to blur, creating a symbiotic relationship where continuous innovation makes financial services faster, more inclusive, and more customer-centric than ever before.
Frequently Asked Questions about Bank-Fintech Integration
Here are answers to the most common questions we hear about fintech integration with banks.
What are the primary benefits for a traditional bank partnering with a fintech?
The primary benefits of fintech integration with banks are transformative. Key advantages include:
- Accelerated Digital Change: Banks can rapidly modernize services and shorten time-to-market for new products by leveraging existing fintech innovation.
- Improved Customer Experience: Integrating intuitive fintech solutions helps banks offer personalized advice and streamlined mobile services, which is critical as 48% of Americans now use mobile banking.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation, improved data analytics, and AI-driven processes lead to significant cost reductions and productivity gains. For instance, some banks have improved loan productivity by 37%.
- Access to New Markets: Partnerships help banks reach unbanked populations (4.2% of US households) and attract younger, digital-native customers.
What are the biggest risks in a bank-fintech partnership?
While beneficial, these partnerships carry significant risks that require careful management.
- Regulatory and Compliance Failures: This is a top concern, as fintechs may not adhere to strict banking regulations like BSA/AML. A staggering 90% of sponsor banks struggle with compliance, sometimes leading to the termination of partnerships.
- Cybersecurity Breaches: Integrating systems expands the potential attack surface, making robust data security and encryption non-negotiable to prevent catastrophic breaches.
- Technical Integration Challenges: Clashes between legacy banking systems and modern fintech APIs are common, leading to costly and complex integration problems. A lack of API experience, cited by 81% of banks, exacerbates this.
- Cultural Clashes: The different operating speeds and risk appetites of banks and fintechs can create friction that derails collaboration. This misalignment is a key reason why only 6% of bank executives felt their partnerships achieved the targeted ROI.
What is Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS)?
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) is a model where a licensed bank uses APIs to “rent out” its regulated infrastructure to other businesses. This allows a non-bank company—like a fintech, e-commerce platform, or retailer—to offer financial products such as checking accounts, debit cards, or loans directly to its customers without needing its own banking license.
The bank handles the complex regulatory, compliance, and security functions in the background. Meanwhile, the partner company focuses on creating a seamless customer experience and integrating the financial service into its own product. BaaS is a key enabler of embedded finance, making financial services more convenient and accessible.
Conclusion
The relationship between banks and fintechs has evolved from competition to a powerful collaboration that is reshaping finance. This symbiotic relationship benefits everyone by combining the trust and scale of banks with the agility and innovation of fintechs.
The lines between banks and fintechs are blurring, creating a new standard for success in the financial industry. This isn’t just a trend; it’s a fundamental shift toward survival and growth. The continuous innovation powered by AI, blockchain, and Web3 technologies is creating possibilities that seemed like science fiction just a few years ago, from invisible payments to tokenized assets.
The numbers confirm this direction. With nearly two-thirds of banks now in fintech partnerships and the global market projected to reach $917 billion by 2032, the collaborative approach is the clear path forward.
This is about creating better, faster, and more inclusive financial experiences for people. When a small business gets a loan in minutes or a person sends money across the world instantly, that’s the real impact of this integration.
At Avanti3, we understand that the future belongs to those who can bridge the worlds of traditional finance and cutting-edge technology. We’re here to help you design that bridge and cross it successfully.






